Setup and Overview of the Tutorial Environment
In this section, we’ll look at the setup of the Kubernetes cluster (Red Hat OpenShift) we’re using for today’s lab. This includes Kubeflow (Red Hat OpenShift AI) that have been installed using the OpenShift operators, as well as the projects that have been created for you. We’ll look at the operators we’ll be using throughout the lab.
1. Exploring the Lab Environment
1.1. Web Console to access Kubernetes
First, let’s ensure we’re logged into the OpenShift cluster through the Web Console. You can access the OpenShift Console from the lab’s start page, or you can visit the OpenShift Console using this OpenShift Web Console.

You’ll be prompted to log in with your credentials, here they are as a reference:
Username:
{user}Password:
{password}Once you’re logged in, you’ll be at the OpenShift dashboard.
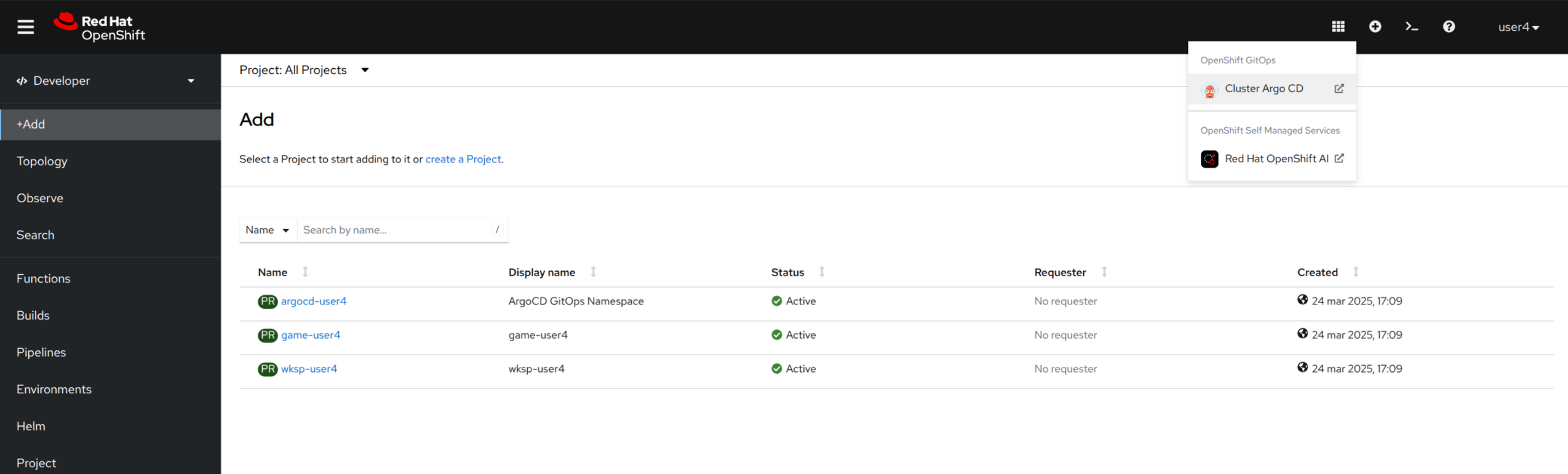
| If you aren’t already, you can navigate to the Developer perspective, where we’ll be spending some of our time. |
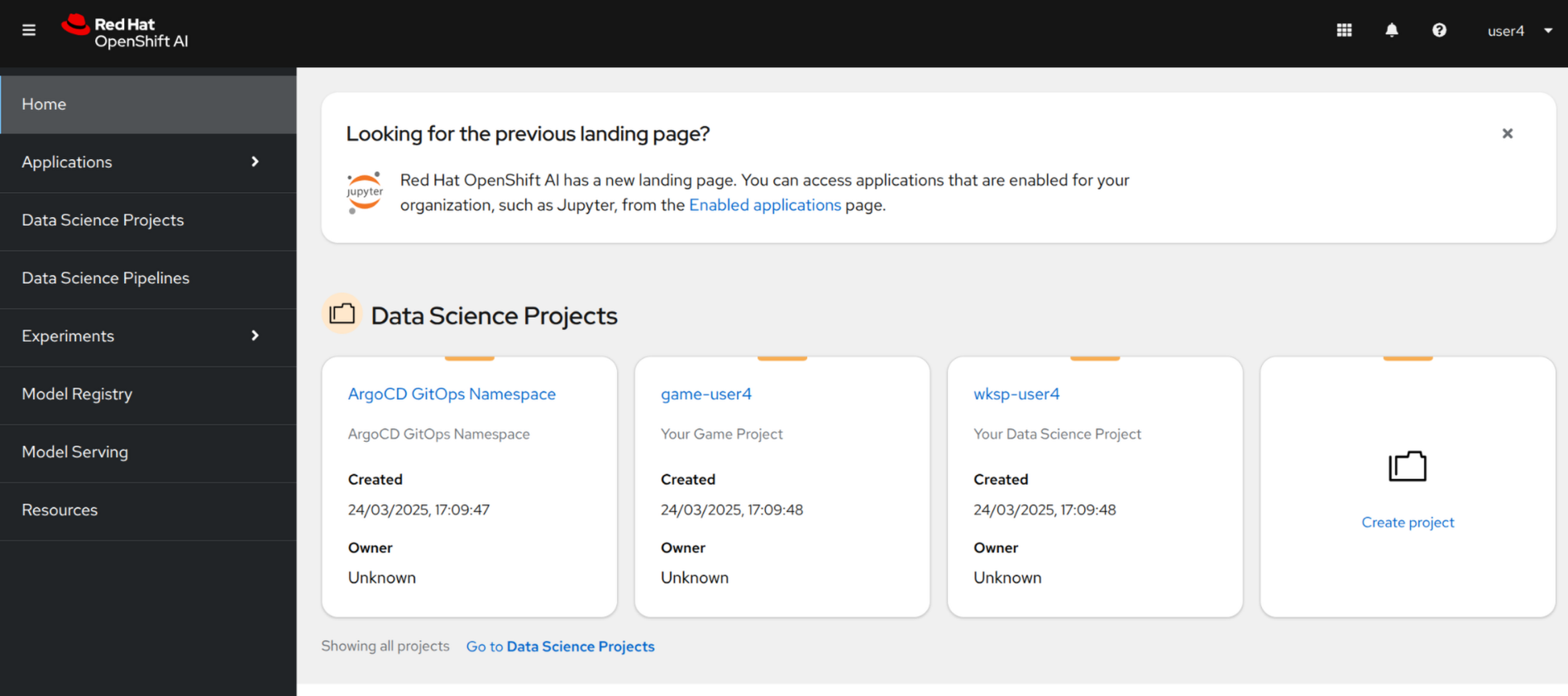
1.2. Access Kubeflow via OpenShift AI
Let’s also view the process of accessing the OpenShift AI. You can access the OpenShift AI dashboard either from the the OpenShift Web Console app launcher, or you can visit the OpenShift AI Console using this OpenShift AI Dashboard.

By logging in with OpenShift you’ll use your same credentials to access OpenShift AI:
-
Username:
{user} -
Password:
{password}
1.3. Gitea
We’ll also be using Gitea, a self-hosted Git service, to store our game code and Argo CD application manifests. To access Gitea, visit this Gitea. You’ll have access to multiple Gitea repositories that contain the source code and Argo CD application manifests. As a reference, here are your credentials:
-
Username:
{user} -
Password:
{password}
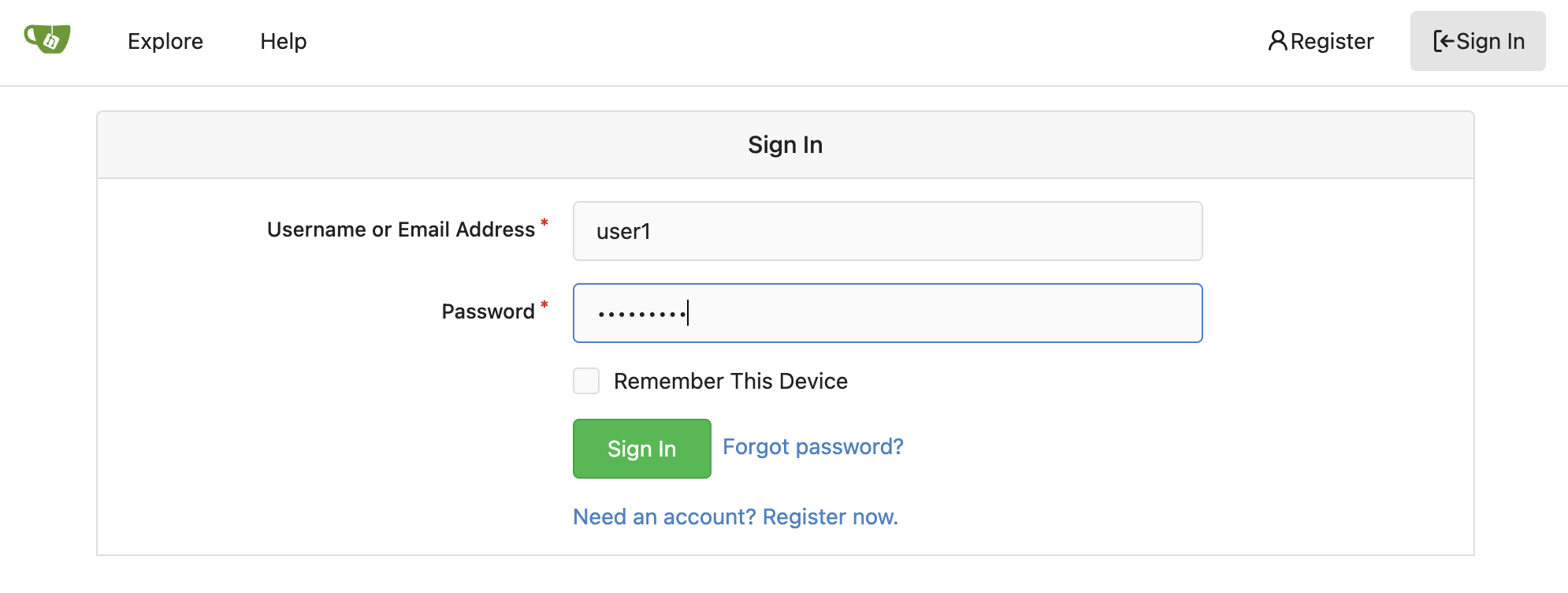
Once logged in, you can access the following source repositories:
We also have a repository that contains the ArgoCD application manifests.