Ansible Kubernetes
In this section, you’ll learn the following:
-
How Ansible connects with Kubernetes
-
Deploying Applications to Kubernetes using Ansible
-
Using Ansible Templates as Kubernetes manifests
-
Deleting Kubernetes Resources
Ansible and Kubernetes
Ansible provides an Ansible Kubernetes Collection to interact with a Kubernetes cluster. With these collections, you get the same approach of maintaining more traditional workloads like virtual machines, but for Kubernetes.
The first thing you need to do is create a Kubernetes cluster. You can use any Kubernetes cluster you might have available (minikube, K3s, EKS, AKS, OpenShift, …) but since there are many options we’ll focus on Red Hat Developers Sandbox a free cloud Kubernetes-OpenShift cluster ready to use, so no local installation is required.
Setup Red Hat Developer Sandbox
Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift is a free Kubernetes cloud environment in a shared, multi-tenant OpenShift cluster that is pre-configured with a set of developer tools. The Developer Sandbox is active for 30 days and renewable once it expires.
To create your account, register to Developer Sandbox for Red Hat OpenShift. From there, click on the red button that says Start your sandbox for free as shown in the following image.
Use your existing Red Hat account or create a new one, then follow the instructions on the screen. You should then be redirected to the Developer Sandbox page again, but this time, you should see a button labelled Start using your sandbox.
Clicking on it opens up the OpenShift login screen where you can log in using the DevSandbox button, as seen below.

Clicking this button opens up your new OpenShift cluster console.
After Kubernetes is up and running, we install the Kubernetes Collection.
Installing Ansible Kubernetes Collection
First of all, we install the Kubernetes Python dependency:
pip install kubernetes
You must use pip3 instead of pip depending on the environment and version.
|
Then let’s use Ansible Galaxy to install the collection:
ansible-galaxy collection install kubernetes.coreStarting galaxy collection install process
Process install dependency map
Starting collection install process
Downloading https://galaxy.ansible.com/download/kubernetes-core-2.4.0.tar.gz to /Users/alexsoto/.ansible/tmp/ansible-local-561757k19pm6z/tmpkia3z432/kubernetes-core-2.4.0-e57tp6bs
Installing 'kubernetes.core:2.4.0' to '/Users/alexsoto/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/kubernetes/core'
kubernetes.core:2.4.0 was installed successfully
If you get a certificate verify failed exception, run the command with the --ignore-certs option.
|
Deploy Application to Kubernetes
To deploy the application, a login process is required.
The collection supports username/password method, kubeconfig folder, and also the authentication token.
For Red Hat Sandbox, we need to use the token approach to login into the cluster and interact with it.
Get the Server Address and the Auth Token
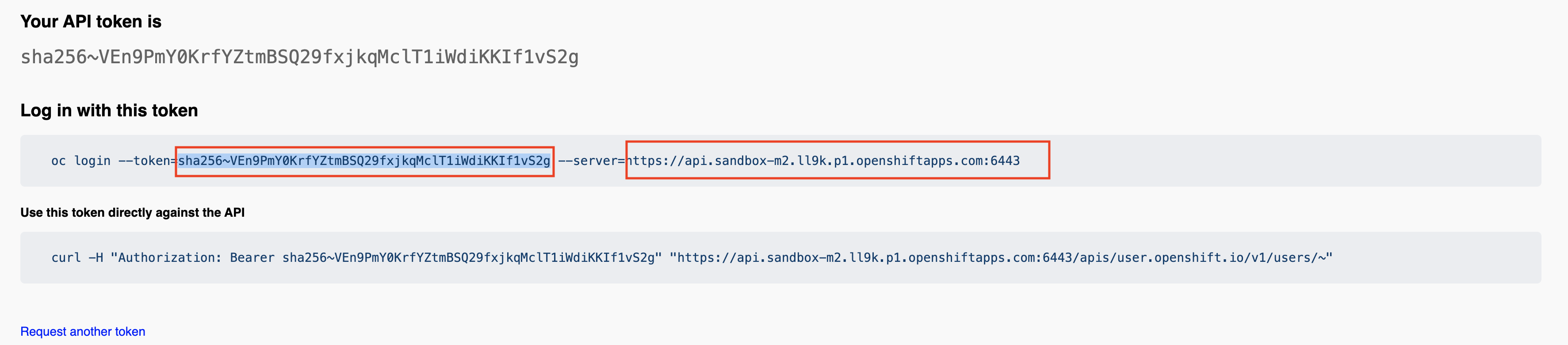
Go to Sandbox main screen, click on your username placed at top-right position, and select the Copy login command option from the drop-down menu.
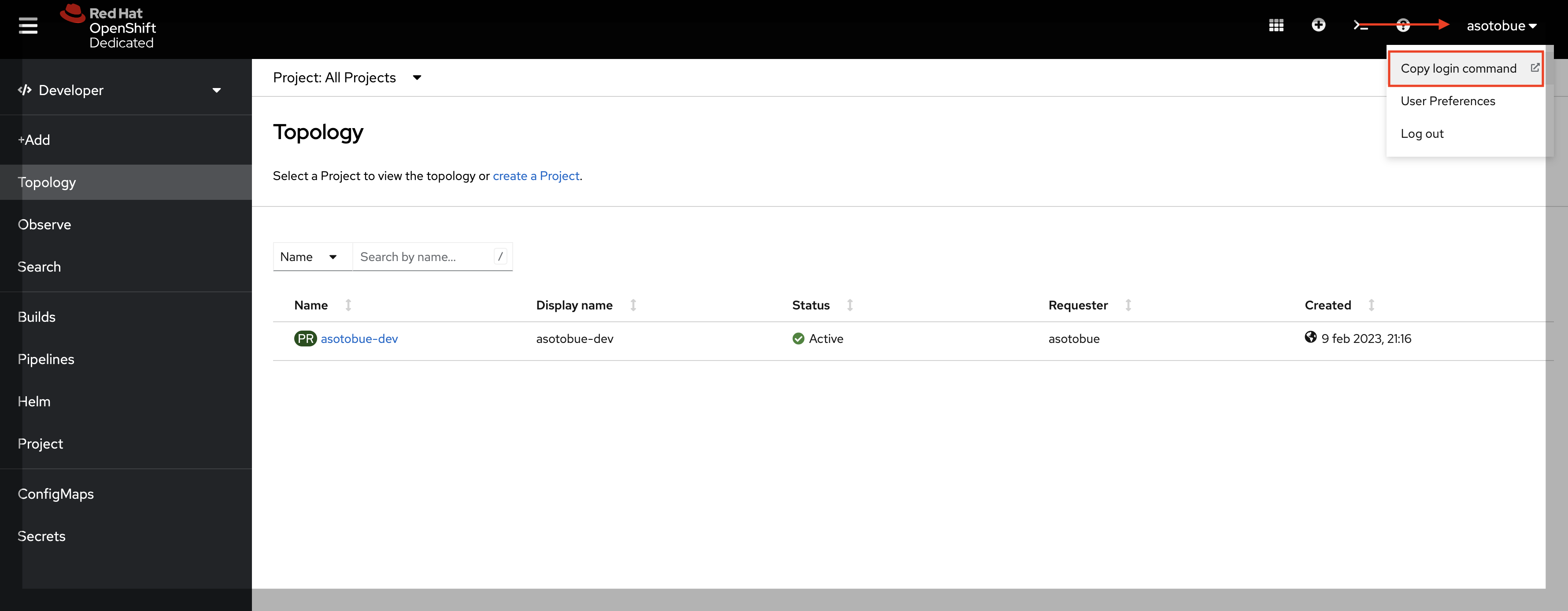
Then, copy the token and server properties in a temporal file, as we’ll need them later.
Current Namespace
Another important data to know is the working namespace Red Hat Sandbox has assigned to us.
It’s in the form of <username>-dev, and you can easily found it in the upper-left corner.
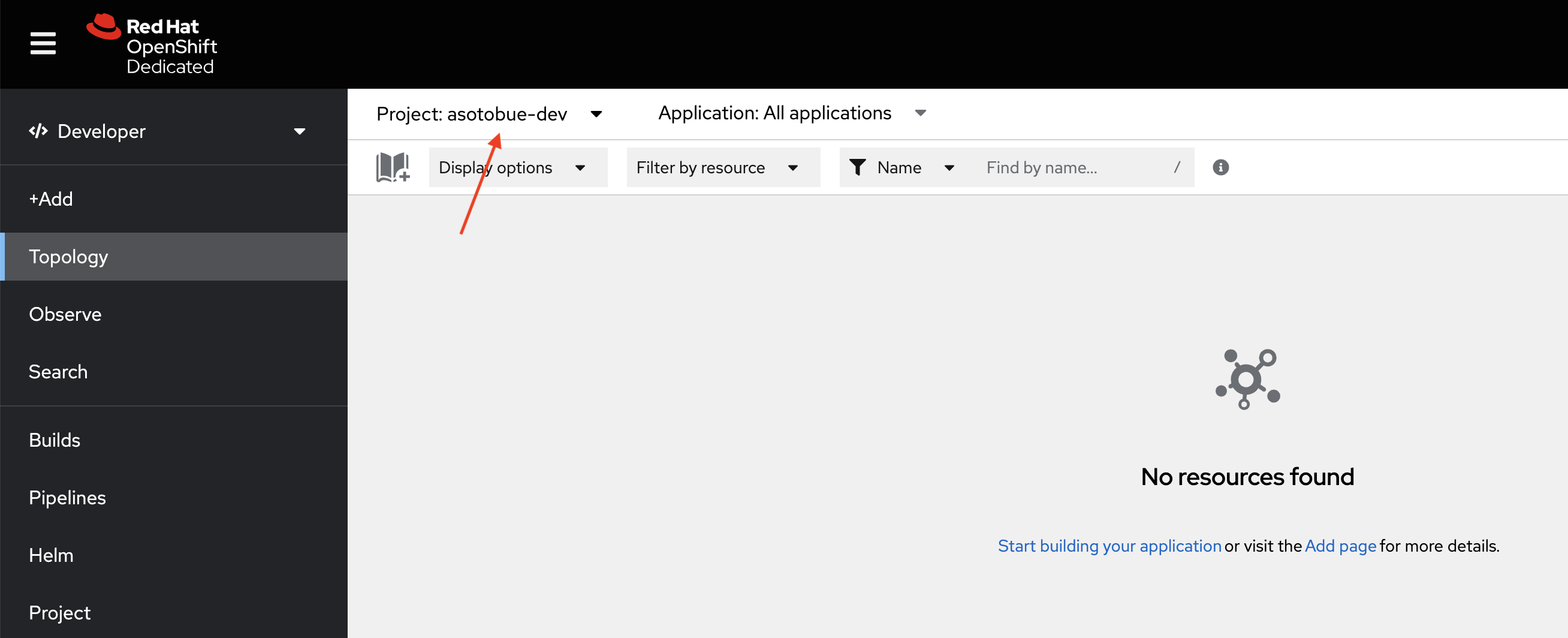
This namespace is important too, as it’s where we’ll deploy the application.
With this information, let’s make Ansible deploy the application.
Deploy to Kubernetes
Let’s start with a simple deployment of an already developed application.
In your working directory, create a new directory named kubernetes:
mkdir kubernetes
cd kubernetesCreate the first-kubernetes-playbook.yaml file containing the cluster information and the Kubernetes manifest information to deploy the application:
- name: Login
hosts: localhost (1)
connection: local
gather_facts: false
environment:
K8S_AUTH_HOST: "https://api.sandbox-m2.ll9k.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443" (2)
K8S_AUTH_API_KEY: "sha256~NRG7aBVOdaRonMJ172H16KrS0Chy--knwpefomLrcZA" (3)
tasks:
- name: Deploy The Application
kubernetes.core.k8s: (4)
state: present (5)
definition: (6)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: asotobue-dev (7)
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: quay.io/lordofthejars/hello-world:1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: hello-world
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http
protocol: TCP| 1 | The playbook is executed in the local machine |
| 2 | Substitute the hostname with your server property |
| 3 | Substitute the token with your token property |
| 4 | Ansible Kubernetes Collection definition |
| 5 | Apply the manifest |
| 6 | Set the Kubernetes manifest content |
| 7 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
After that, run the following command in the terminal to deploy the application to the Kubernetes cluster:
ansible-playbook first-kubernetes-playbook.yaml[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [Login] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Deploy The Application] **********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0To validate the deployment, access the Red Hat Sandbox Topology view, and check that the application is there up and running:
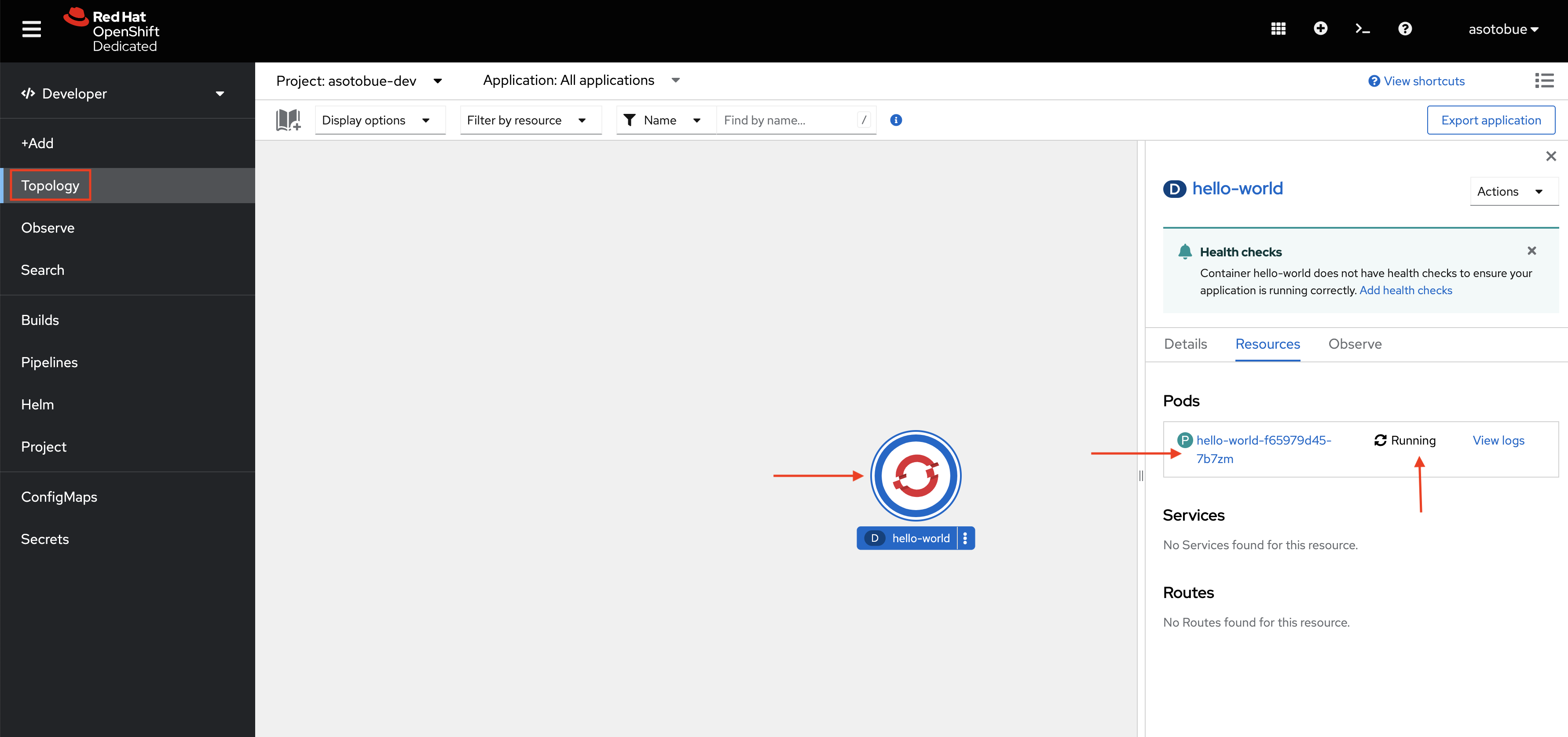
Clean up the Namespace
To clean up the namespace, we need to undeploy the application.
Create a delete-kubernetes-playbook.yaml file selecting which resource is deleted and setting the state to Absent.
- name: Login
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
environment:
K8S_AUTH_HOST: "https://api.sandbox-m2.ll9k.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443" (1)
K8S_AUTH_API_KEY: "sha256~NRG7aBVOdaRonMJ172H16KrS0Chy--knwpefomLrcZA" # (2)
tasks:
- name: Delete The Application
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: absent (3)
api_version: v1
kind: Deployment
namespace: asotobue-dev (4)
name: hello-world (5)| 1 | Substitute the hostname with your server property |
| 2 | Substitute the token with your token property |
| 3 | Delete the resource |
| 4 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
| 5 | Name of the deployment |
After that, run the following command in the terminal to undeploy the application from the Kubernetes cluster:
ansible-playbook delete-kubernetes-playbook.yaml[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [Login] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Delete The Application] **********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0Referencing Kubernetes manifest files
In the previous example, we defined the Kubernetes manifest within the playbook. Although this is possible and it has some advantages, most of the time, you’ll define the resources outside of the playbook. Ansible Kubernetes collection let you reference external Kubernetes files directly in the playbook.
Create a Kubernetes Deployment file named deployment.yaml in kubernetes directory with the following content:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: asotobue-dev (1)
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: quay.io/lordofthejars/hello-world:1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: hello-world
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
namespace: asotobue-dev (2)
annotations:
app.quarkus.io/commit-id: 277270f3f2a7b0e78c69b3be83be372c7e6ca693
app.quarkus.io/build-timestamp: 2023-03-08 - 08:51:15 +0000
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
name: hello-world
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
type: ClusterIP| 1 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
| 2 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
Then, create the file-kubernetes-playbook.yaml file referencing this manifest instead of defining it on the playbook.
- name: Login
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
environment:
K8S_AUTH_HOST: "https://api.sandbox-m2.ll9k.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443" (1)
K8S_AUTH_API_KEY: "sha256~NRG7aBVOdaRonMJ172H16KrS0Chy--knwpefomLrcZA" (2)
tasks:
- name: Deploy The Application
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: present
src: deployment.yaml (3)| 1 | Substitute the hostname with your server property |
| 2 | Substitute the token with your token property |
| 3 | Set the location of the Kubernetes manifest to apply |
After that, run the following command in the terminal to undeploy the application from the Kubernetes cluster:
ansible-playbook file-kubernetes-playbook.yaml[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [Login] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Deploy The Application] **********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0Check the application is running in the Red Hat Sandbox Topology view:
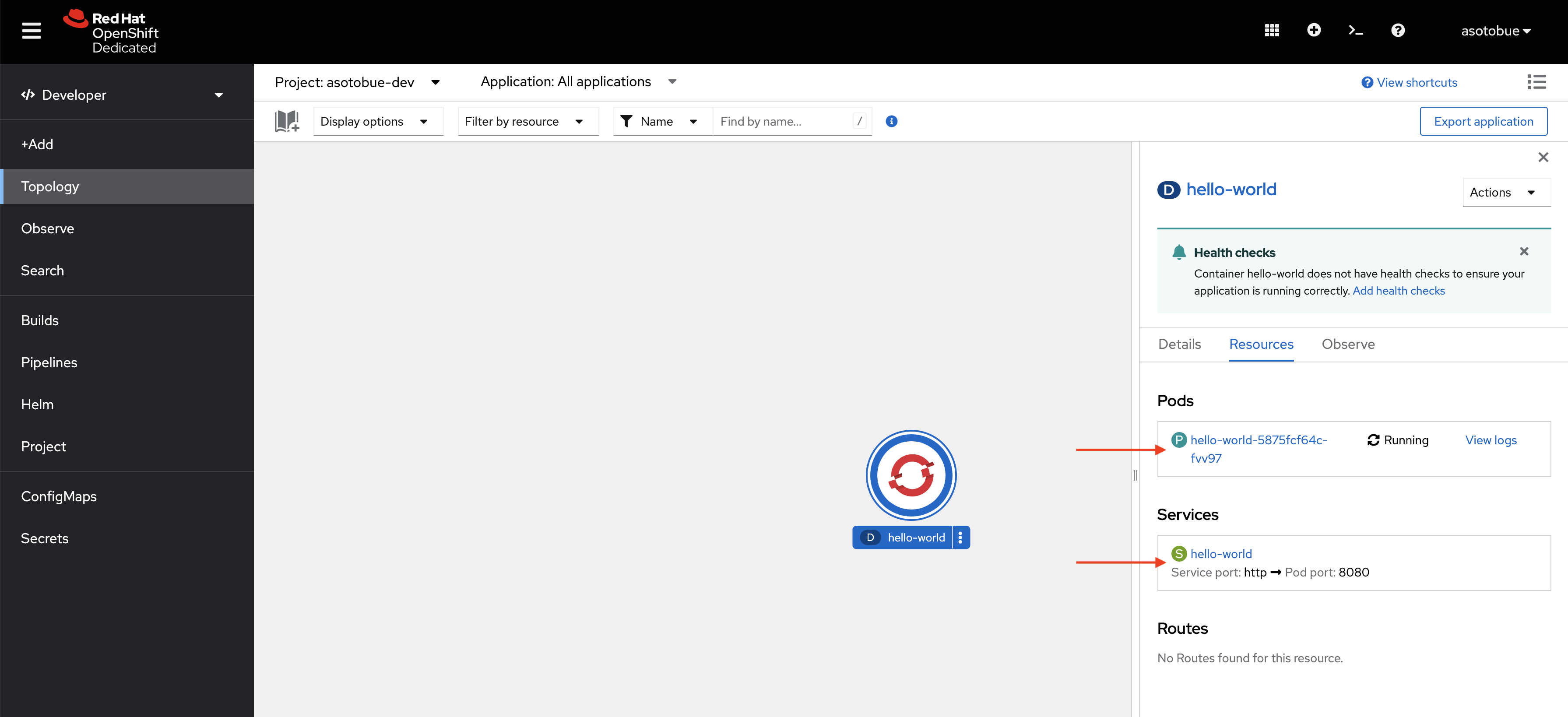
Clean up
To cleanup the namespace, create the delete-all-kubernetes-playbook.yaml:
- name: Login
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
environment:
K8S_AUTH_HOST: "https://api.sandbox-m2.ll9k.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443" (1)
K8S_AUTH_API_KEY: "sha256~NRG7aBVOdaRonMJ172H16KrS0Chy--knwpefomLrcZA" (2)
tasks:
- name: Delete The Application
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: absent
api_version: v1
kind: Deployment
namespace: asotobue-dev (3)
name: hello-world
- name: Delete The Service
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: absent
api_version: v1
kind: Service
namespace: asotobue-dev (4)
name: hello-world| 1 | Substitute the hostname with your server property |
| 2 | Substitute the token with your token property |
| 3 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
| 4 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
And run the playbook:
ansible-playbook delete-all-kubernetes-playbook.yamlAnsible Templates as Kubernetes manifests
Ansible Kubernetes Collection also integrates with Ansible templates, so you can define Kubernetes manifests as templates.
Create a deployment.j2 file in the kubernetes folder:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: asotobue-dev (1)
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ version }} (2)
name: hello-world
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ version }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: hello-world
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ version }}
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: quay.io/lordofthejars/hello-world:{{ version }}
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: hello-world
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http
protocol: TCP| 1 | Substitute the namespace with your current working namespace |
| 2 | Template placeholder |
Then, create the template-kubernetes-playbook.yaml file:
- name: Login
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
vars:
- version: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT (1)
environment:
K8S_AUTH_HOST: "https://api.sandbox-m2.ll9k.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443" (2)
K8S_AUTH_API_KEY: "sha256~NRG7aBVOdaRonMJ172H16KrS0Chy--knwpefomLrcZA" (3)
tasks:
- name: Deploy The Application
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: present
template: deployment.j2 (4)| 1 | Set version for the placeholder |
| 2 | Substitute the hostname with your server property |
| 3 | Substitute the token with your token property |
| 4 | Set the template location |
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook template-kubernetes-playbook.yaml[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [Login] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Deploy The Application] **********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0Check the application is running in the Red Hat Sandbox Topology view:
