Call Center - Intro and Use Case
This is an advanced Decision Model & Notation lab that introduces DMN Decision Services, Relations, nested boxed expressions, etc. It also explores a number of different FEEL constructs and expressions like, for example, list contains.
Problem Statement
In this lab we will create a decision that determines if a call-centre can take an incoming call. Whether a call will be accepted by a certain office depends on:
-
The office accepts the call.
-
There are employees currently available at the office.
Whether the office can accepts a call depends on: whether the phone number has been banned. the purpose of the phone call ("help" or "objection").
Create a new decision
To work in the decision model, we’ll use the KIE Sandbox DMN editor. 1. In your browser, navigate to http://dmn.new/
-
Click on the Untitled tile to define the DMN model name. Give it the name
call-centre. This will create the asset and open the DMN editor.
Next Steps
You can do this lab in 2 ways:
-
If you already have (some) DMN knowledge, we would like to challenge you to build the solution by yourself. After you’ve built solution, you can verify your answer by going to the next module in which we will explain the solution and will deploy it onto the runtime.
-
Follow the step-by-step below which will guide you through the implementation.
Authoring the decisioning for the Call Center
The problem statement describes a number of different inputs to our decision:
-
Call: the incoming call into the call-centre
-
Employees: the employees of certain office.
-
Office: an office to which the call could potentially be routed.
Furthermore, the problem statement describes that phone numbers could be banned. So, also banned numbers can be regarded as an input to our model (although we will not implement it as an input in this lab).
With the given input, we need to make the following decisions:
-
Accept Call: the final decision we need to make is whether the given office will accept the call.
-
Can Handle Call: whether the office can actually accept the call. As defined in the problem statement, this depends on:
-
whether the phone number has been banned;
-
the purpose of the phone call (“help” or “objection”).
Accept Call Decision Structure
-
Accept Call: the final decision we need to make is whether the given office will accept the call.
-
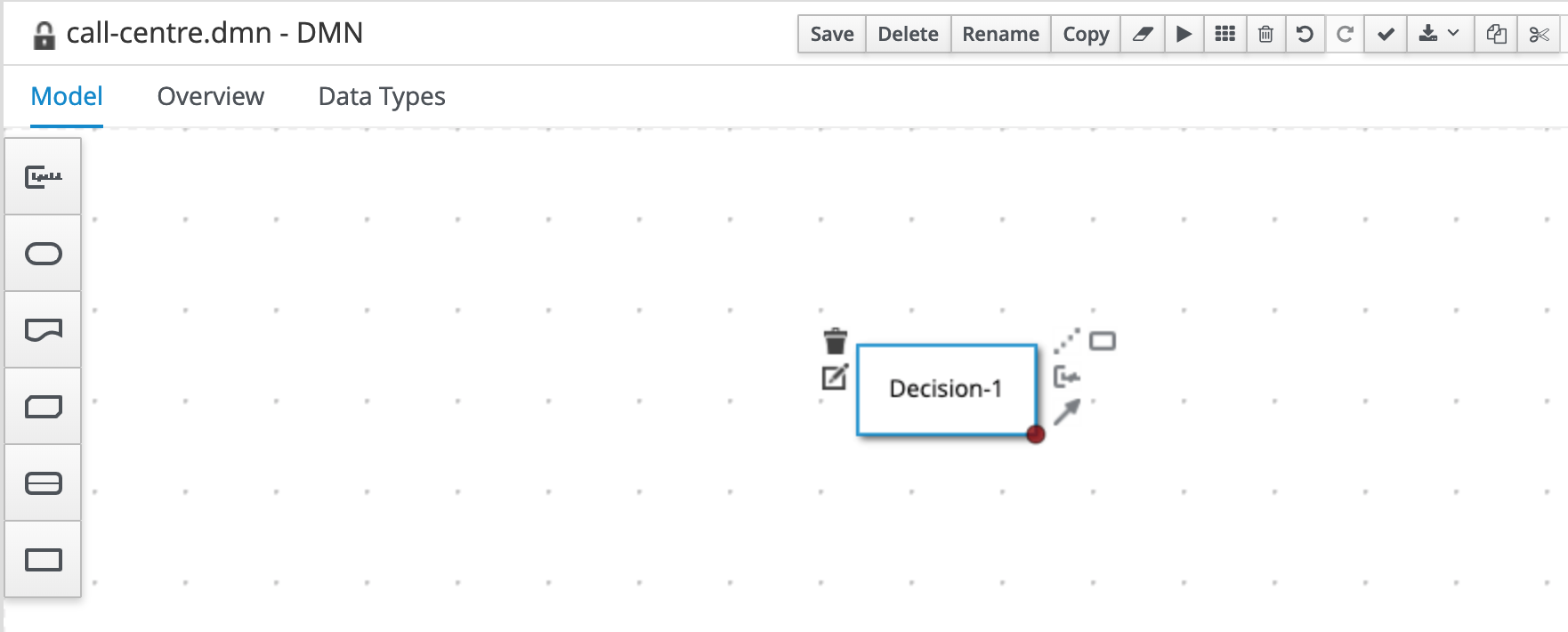
Add a Decision node to the diagram by clicking on the Decision node icon and placing it in the DRD.
-
Double-click on the node to set the name. We will name this node
Accept Call. -
With the
Accept Callnode selected, open the property panel. Set the Output data type toboolean.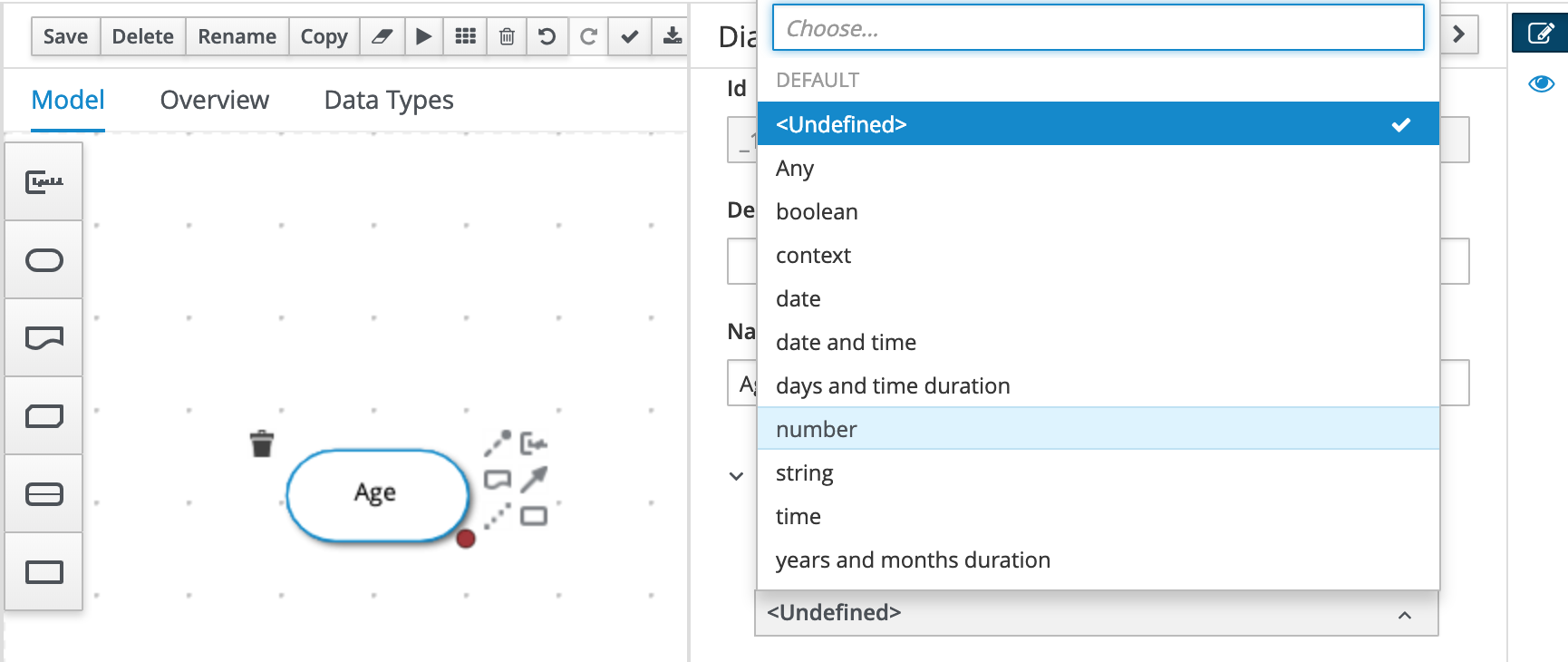
-
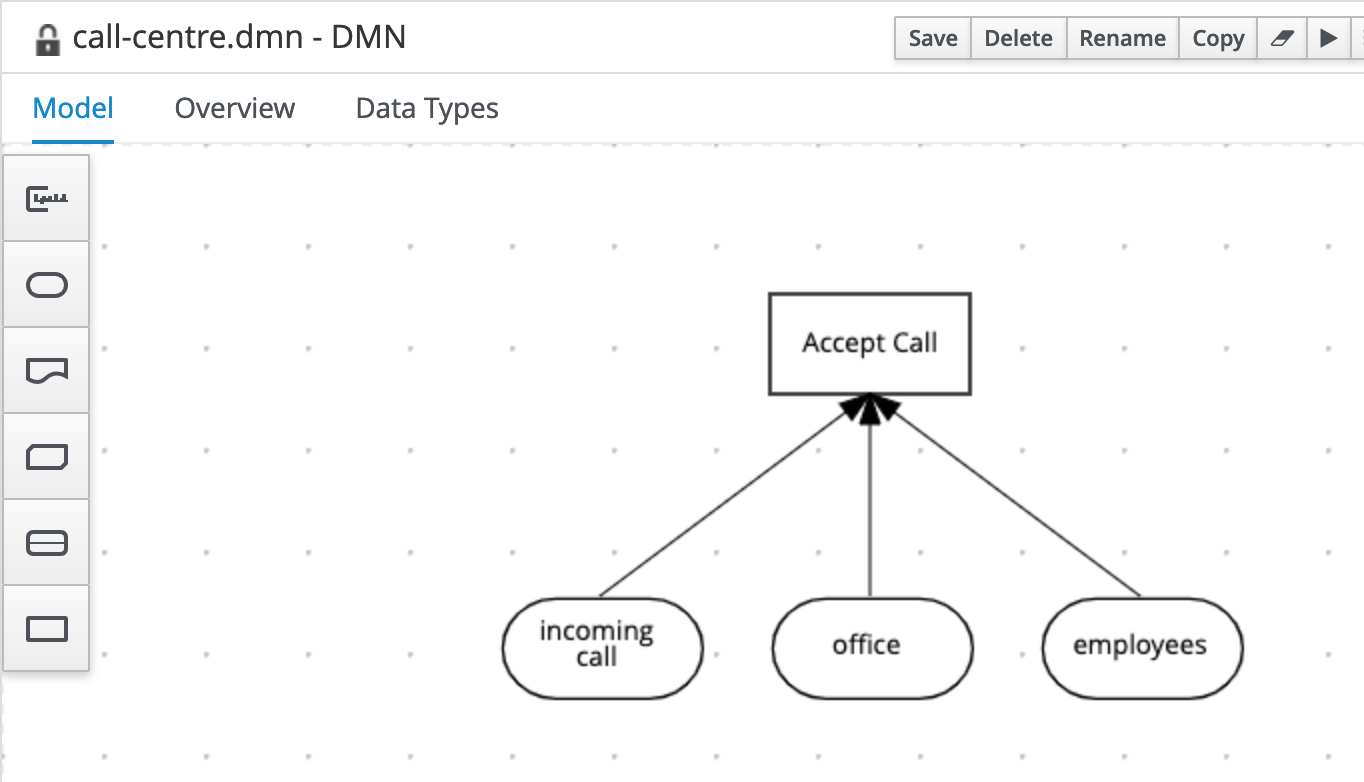
The input of this decision is the incoming call, office and employee. Create these 3 input nodes and connect them to the Accept Call decision.
-
We can now set data types of our input nodes.
-
Click on the
incoming callnode, open the property panel and in the Output data type section and click on the Manage button. This will open the Custom Data Types window. -
In the Custom Data Types window, click on the + Add button.
-
Define the data type
tPhoneNumberas follows:
-
Define another data type
tCallas follows. Note that this datatype has a field that is of typetPhoneNumber, the type we defined earlier:
-
When you’ve created the
tCalltype, go back to the DRD by clicking on the Model tab. -
Select the
incoming callnode, and in the property panel, set the node’s Output data type totCall
-
Next, define the following data type and set it as the Output data type of the
officeinput as such: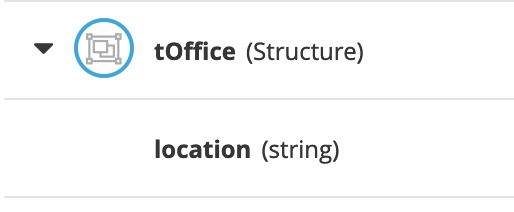
-
Define the data type for
employeesas follows. Note that we’ve first defined the typetEmployee, and afterwards we’ve definedtEmployeesas aListoftEmployee.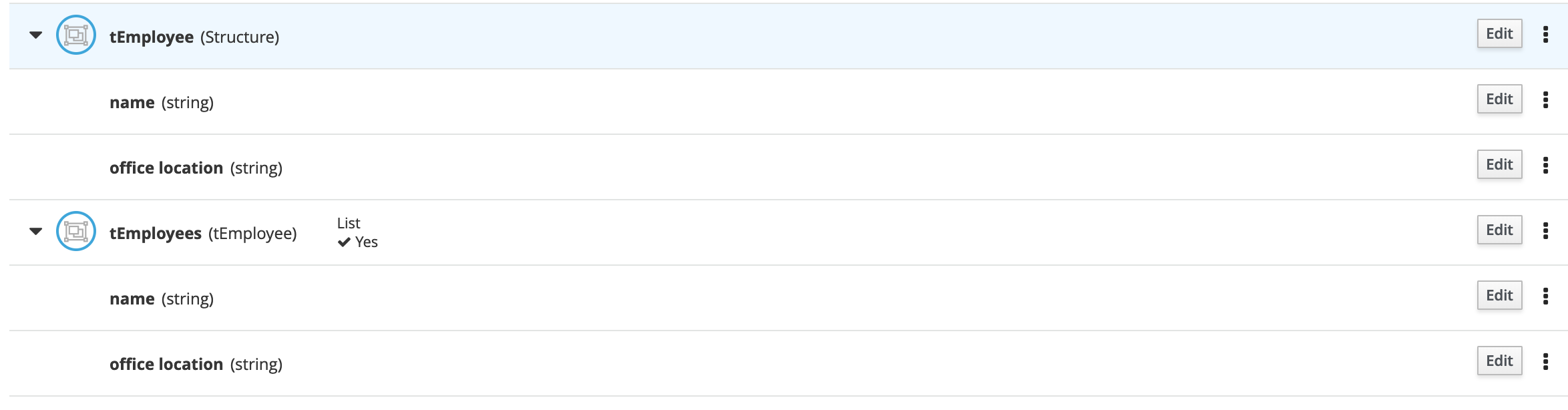
-
Decision Service
With the main structure defined, we can now look at the requirements of the decision whether the office can actually accept the call. As defined in the problem statement, this depends on:
-
whether the phone number has been banned.
-
the purpose of the phone call ("help" or "objection").
We will model this decision as a DMN Decision Service that can be called by our main decision Accept Call.
-
First, model the Decision Service in the DRD and give it the name
Can Handle Call. Set it’s Output data type toboolean.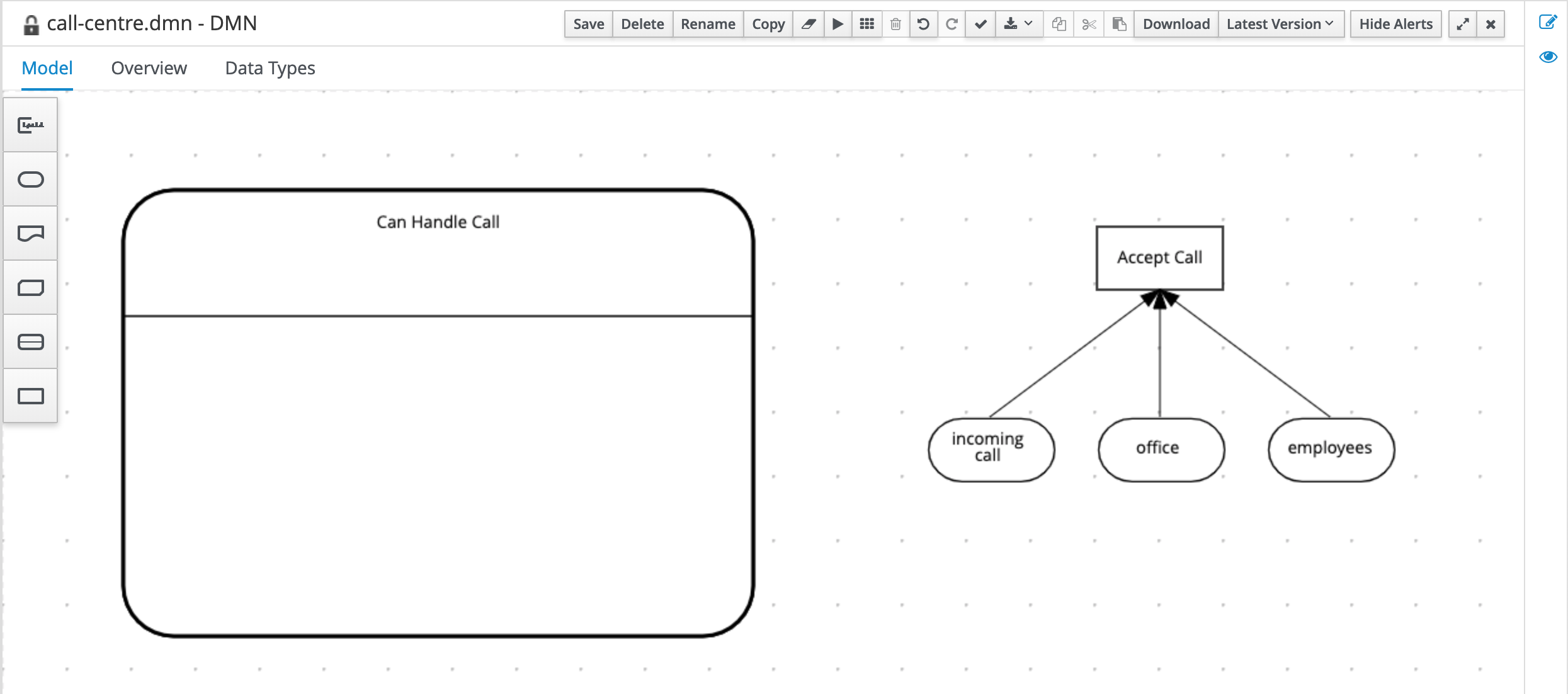
-
Add a Decision Node to the Decision Service. Name it
Call Can Be Handledand set it’s Output data type toboolean.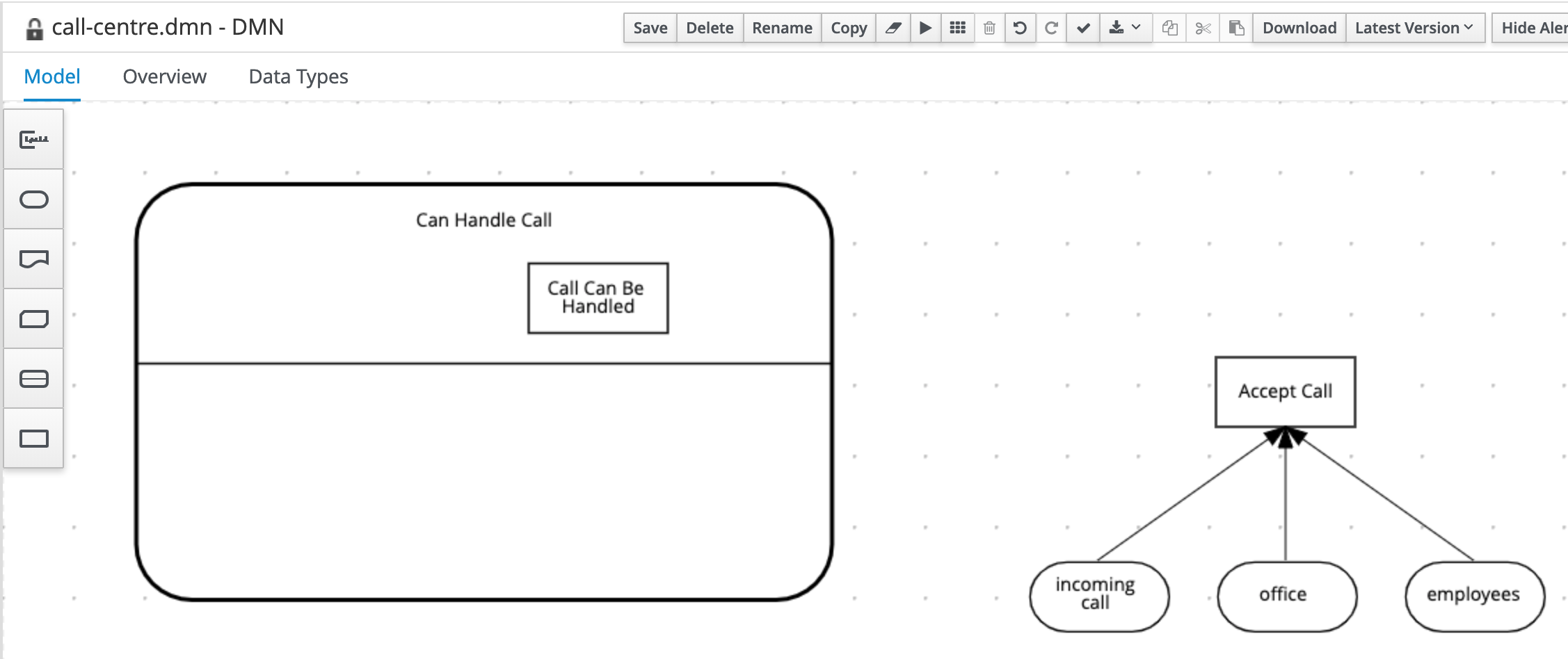
-
Add 2 additional Decision Nodes and name them
Is BannedandCall Purpose Accepted. Both should have an Output data type of typeboolean. -
Connect the 2 Decision Nodes to the
Call Can Be Handlednode.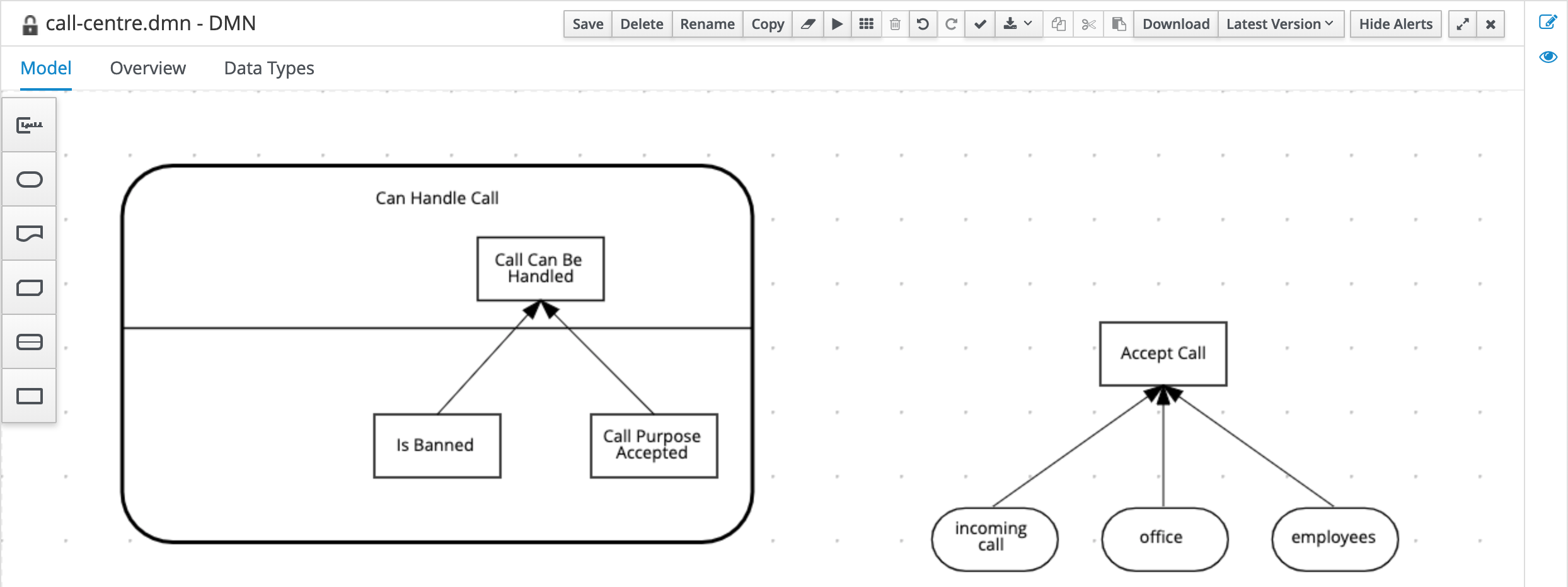
-
The input to both the
Is BannedandCall Purpose Accepteddecisions is acall. Connect the existing node "incoming call" to the 2 decision nodes.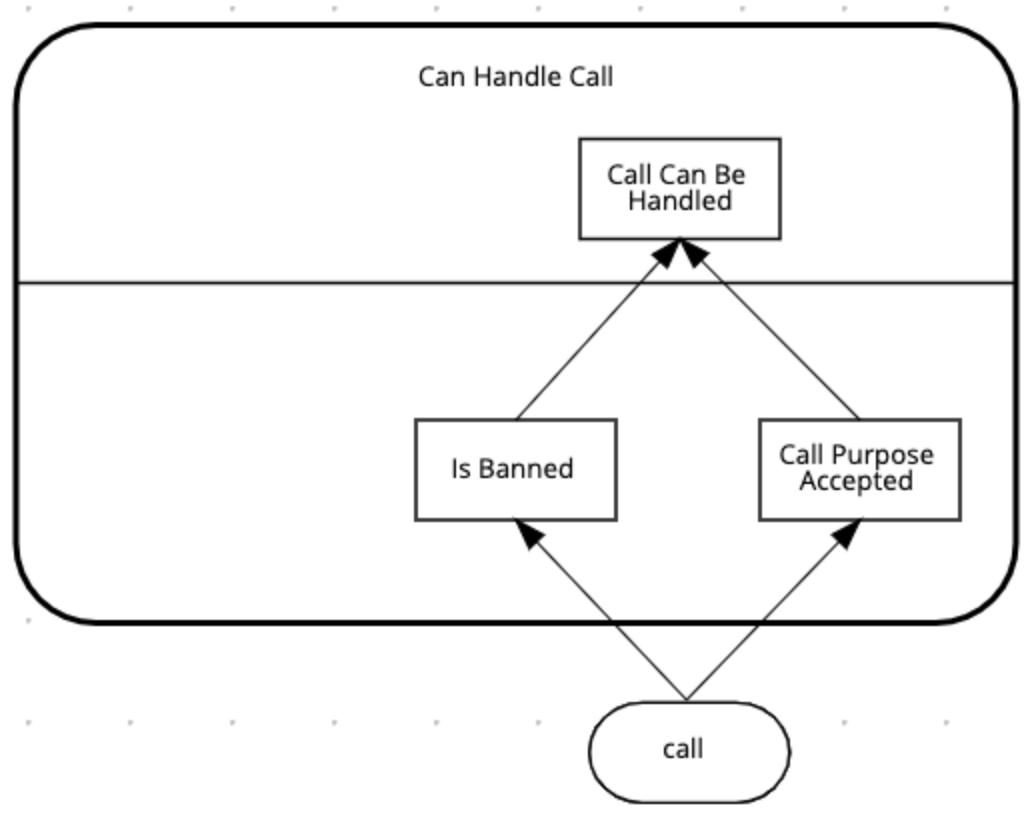
-
The
Is Banneddecision also needs a collection of banned phone numbers. Instead of implementing this as an Input node, we will implement this as a DMN Relation Decision. -
Create a new Decision Node and name it
Banned Phone Numbers. Connect it to theIs Banneddecision node.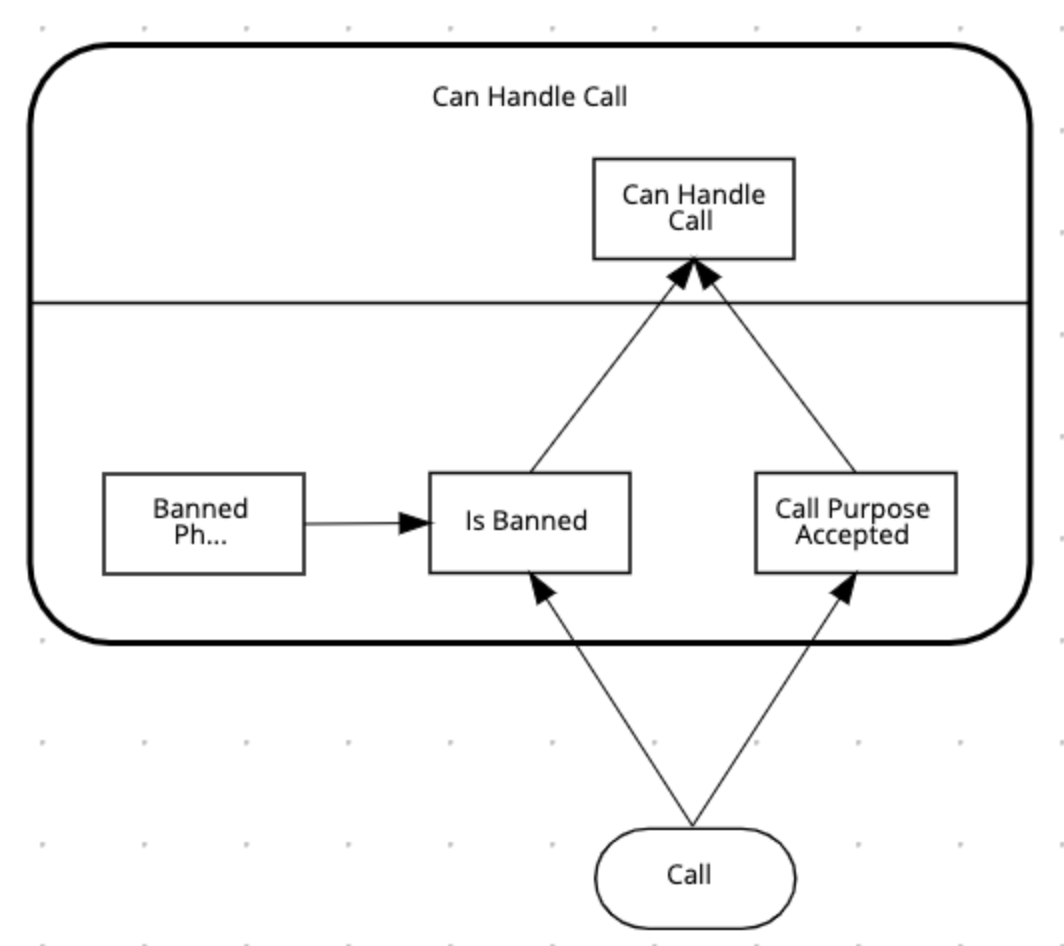
-
The Ouput data type of this nodes is a new custom data type, which is a list of
tPhoneNumber. We’ll name this typetPhoneNumbers: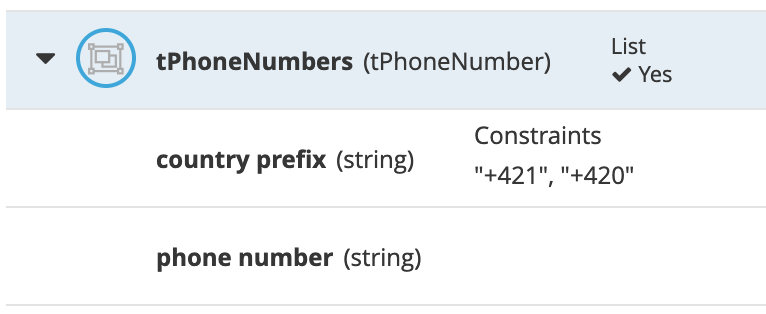
-
Click on the Edit button of the
Banned Phone Numbersnode. Set the logic type of the decision toRelation. Create the following table: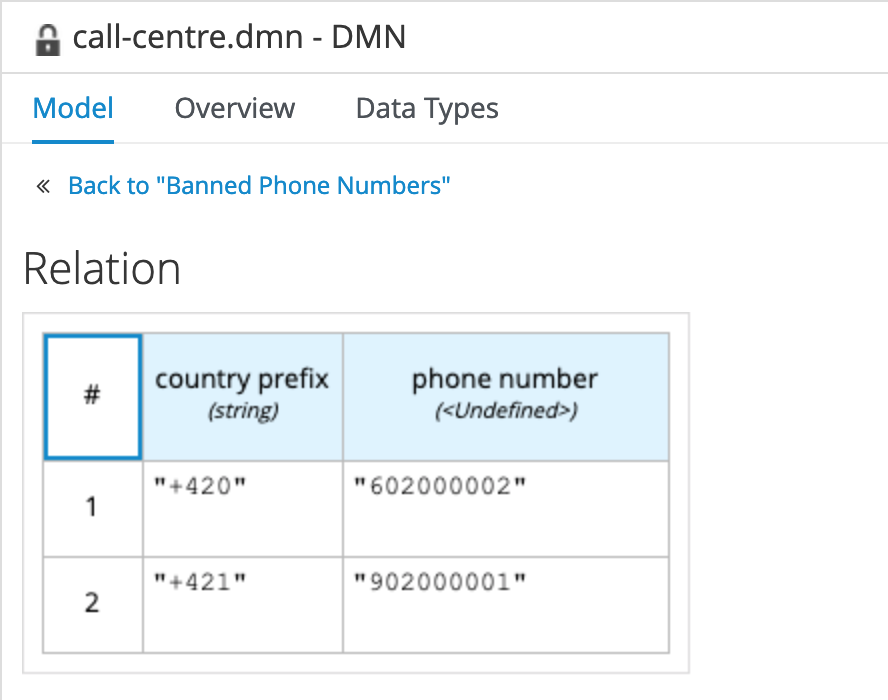
-
We can now implement the logic of the
Is Banneddecision. Click on the Edit button of the decision node. We will implement the logic as a Literal Expression. Define the following FEEL expression:~~~ list contains(Banned Phone Numbers, call.phone) ~~~
-
The next node for which we want to implement the decision logic is
Call Purpose Accepted. Click on the node, and click on the Edit button. Implement the following logic as a Decision Table: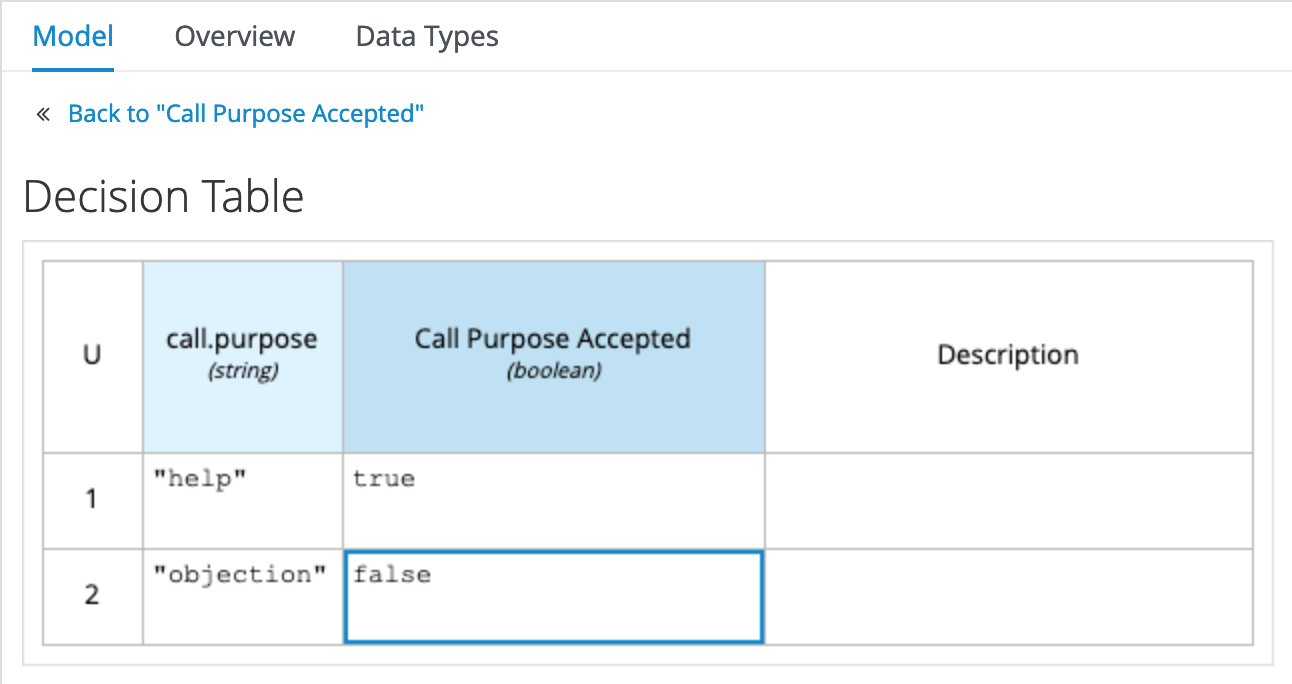
-
We can now implement the decision of
Call Can Be Handled. Click on the node and click on the node’s Edit button. In the decision editor, set the logic type to Decision Table and implement the following table: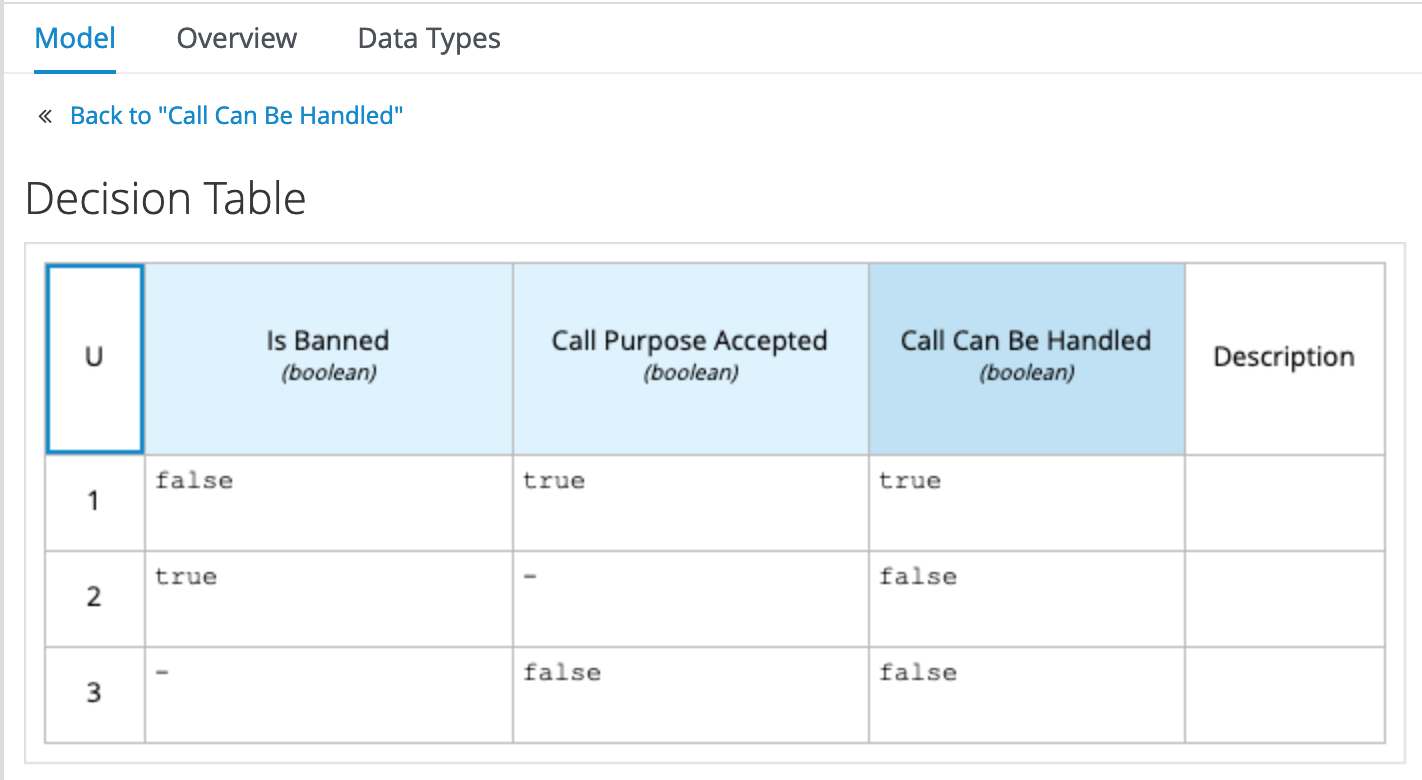
-
Create a DMN Knowledge Requirement from the
Can Handle Calldecision service to theAccept Calldecision.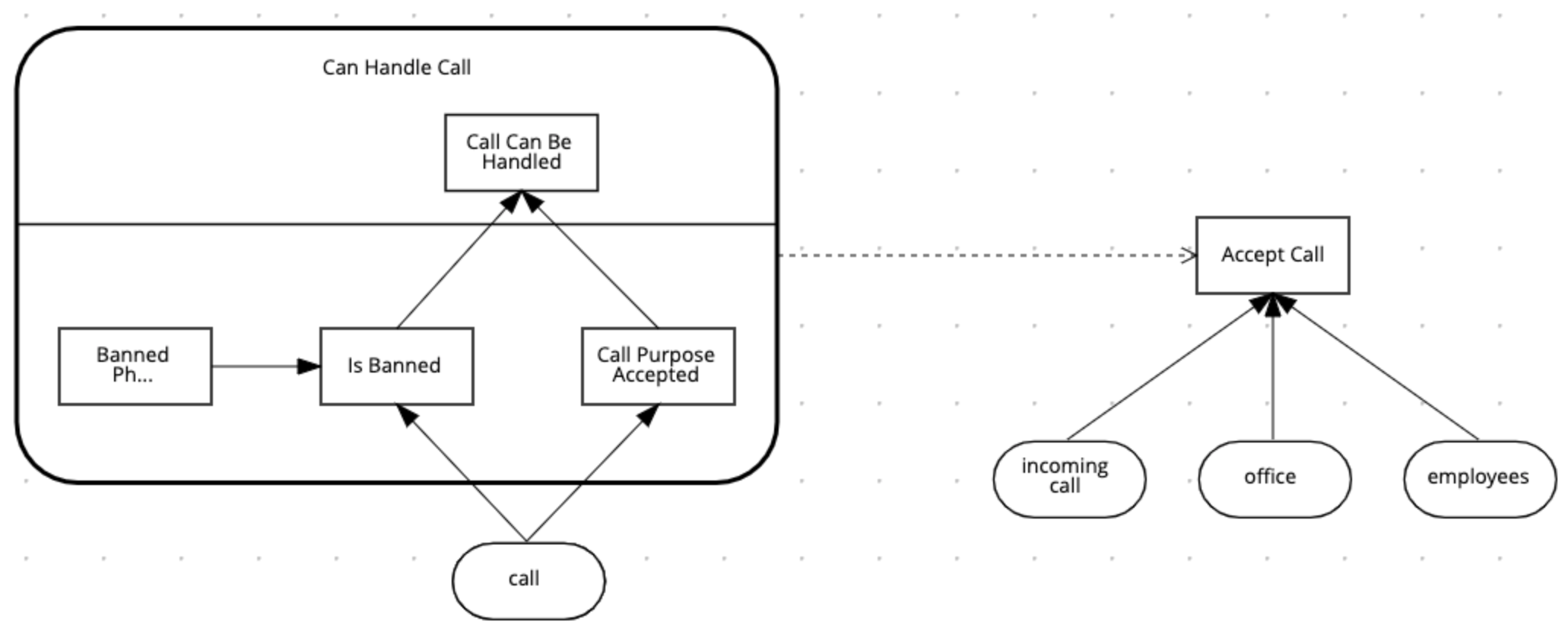
## 7.3. "Accept Call" Decision Logic
-
Implement the
Accept Calldecision logic as follows.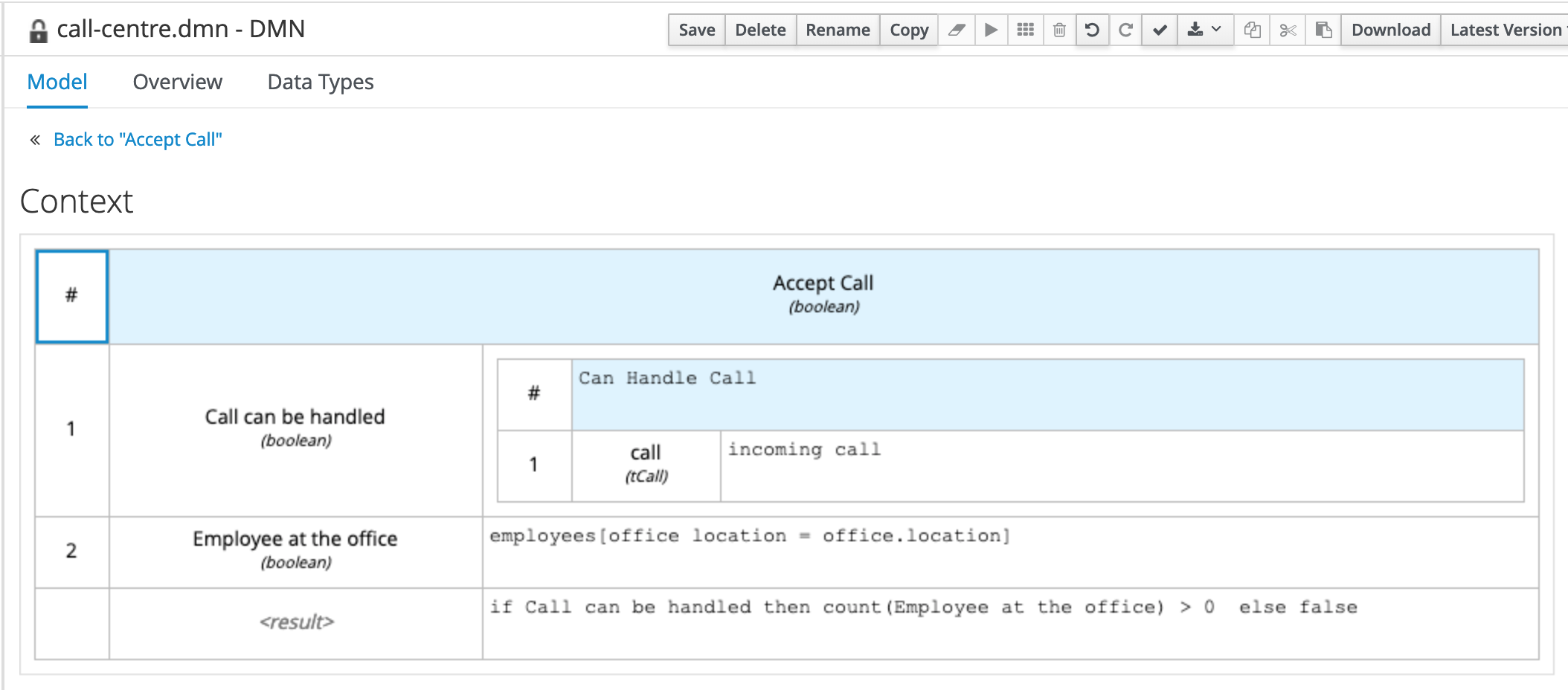
Notice that the line 1 is the invocation of the decision service "Can Handle Call". This is an Invocation of the
Can Handle Callservice, passing theincoming callinput as the variablecall. The output of this invocation will be thebooleanvariableCall can be handled.
The Call can be handled variable as then used to validate the decision result in the last line.