High Level Architecture
Below diagram illustrates the architecture of Red Hat OpenShift Database Access Operator (RHODA)
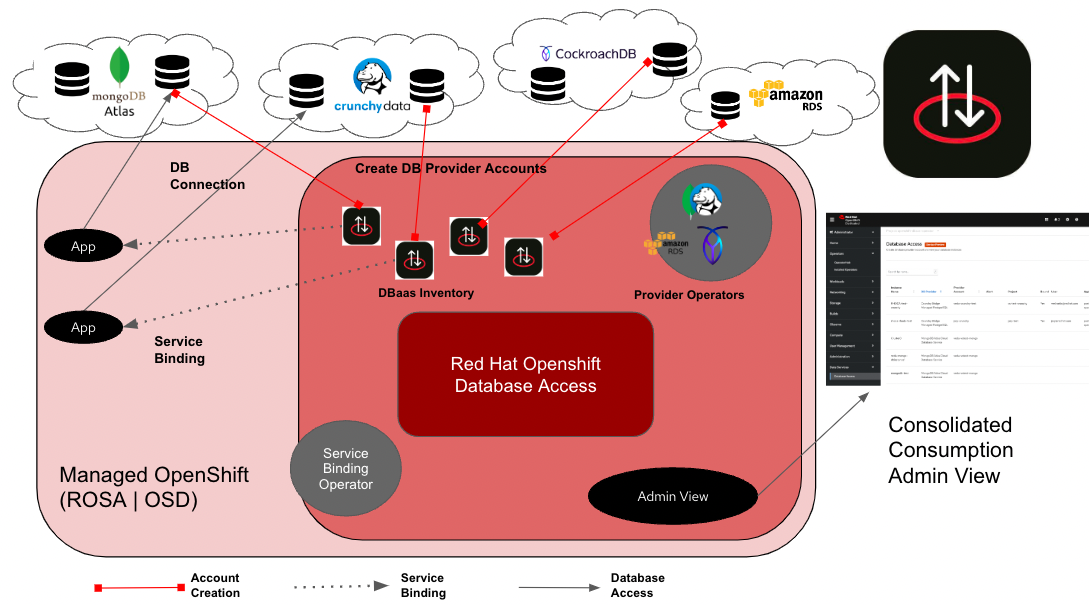
RHODA leverages the Kubernetes construct of operators to bind application clusters to database instances. IT operations can launch a database discovery process based on resource permissions to identify the database instances that can be accessed. Once established, developers can see these new database services from the catalog on their OpenShift developer console represented as a UI tile for each database registered with the system. After selecting a database service instance, the developer can drag and drop a binding connector on the OpenShift developer UI to establish database connectivity to a Kubernetes pod.